Overview & Challenges
The ServiceNow Configuration Management Database (CMDB) plays a critical role across IT operations. It informs incident response, drives change management, supports security investigations and underpins compliance reporting. However, in most enterprise environments today, the CMDB struggles to keep pace with the reality of modern infrastructure.
Assets are often discovered through disjointed tools and partial integrations, resulting in incomplete coverage across infrastructure and services. Ownership and governance information are frequently missing or outdated, making it difficult to determine who is responsible for what. Dependency visibility is limited or entirely absent, leaving teams blind to how assets relate to one another when incidents or changes occur.At the same time, many organizations lack meaningful CMDB metrics. Without a clear way to measure accuracy or completeness, CMDB health becomes subjective rather than data driven. Even when ServiceNow is tightly integrated into IT service management (ITSM) workflows, the underlying CMDB often remains only partially aligned, weakening the value of incident, change and problem management processes that depend on it.
As these gaps accumulate, the CMDB gradually drifts away from reality. Teams lose confidence in the data, automation becomes unreliable and the CMDB shifts from being a system of record to a system of assumption.
What It Teams Are Looking For
To restore trust in the CMDB, IT teams are looking for a fundamentally different approach: one that removes operational burden while increasing confidence in the data.
They want unified discovery across multiple sources that reflects what is actually present in the environment, without requiring teams to deploy and maintain additional tooling. They need clear asset dependency visibility so decisions can be made faster and with less risk during incidents and changes. Most importantly, they want the CMDB to function as a true, authoritative system of record grounded in evidence rather than manual upkeep.
Infoblox addresses these needs by correlating ServiceNow CMDB data with authoritative, network-based discovery, giving IT teams visibility they can trust without adding complexity. The result is a CMDB that works for IT, rather than one IT must constantly work to maintain.
Infoblox Approach To CMDB Reconciliation
Infoblox addresses this challenge by bringing measurable, evidence-based reconciliation to ServiceNow CMDB data with Infoblox Universal Asset Insights™. By analyzing CMDB records against Infoblox’s authoritative asset inventory built from continuous, network-based discovery, organizations gain a clear, objective understanding of how accurately their CMDB reflects what is actually running on the network.
Rather than treating CMDB accuracy as a best-effort or periodic cleanup activity, Infoblox transforms it into a quantifiable outcome. Assets observed on the network are compared directly with ServiceNow records, exposing where the two align and where they diverge. This removes ambiguity and replaces assumptions with verifiable insight.
Configuring the ServiceNow Provider
ServiceNow CMDB reconciliation starts by configuring ServiceNow as a provider in Infoblox using secure, scoped credentials. The integration is one-directional, syncing CMDB data from ServiceNow into Infoblox for analysis, with no data written back to ServiceNow.
Once configured, Infoblox retrieves selected CMDB classes and maps them to its asset inventory. Reconciliation runs automatically, providing continuous visibility into CMDB accuracy.
A step-by-step walkthrough is available in the deployment guide.
ServiceNow discovery configuration can be reviewed in ServiceNow under Configuration > Networking > Discovery > Integration.
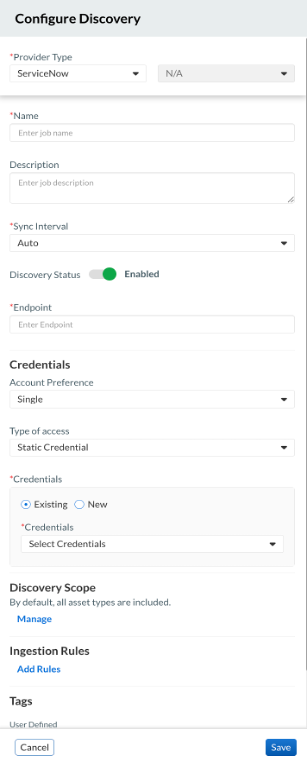
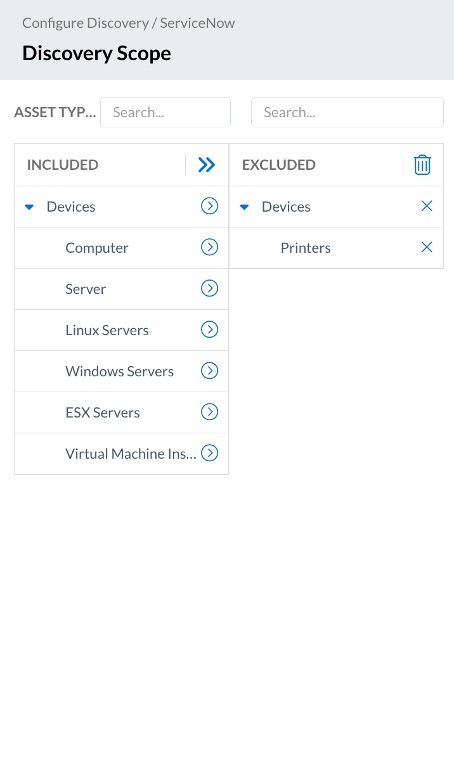
Figure 1. Discovery job configurations
Refer to the deployment guide for detailed, step-by-step instructions on configuring the discovery job.
ServiceNow CMDB Permissions for Reconciliation
Infoblox requires read-only access to ServiceNow CMDB data to perform reconciliation. The integration is non-intrusive and does not write data back to ServiceNow.
A dedicated ServiceNow service account with the cmdb_read role is typically sufficient, providing read access to the cmdb_ci table and its derived classes. Administrators should also ensure that any custom ACLs do not restrict access to required CI records.
This least-privilege approach enables full CMDB visibility while maintaining strong security and governance controls.
ServiceNow CMDB Classes Included in Reconciliation
Infoblox synchronizes data from key ServiceNow CMDB tables to ensure accurate reconciliation against network-observed assets. The integration pulls from the core cmdb_ci table and selected subclasses that represent commonly deployed infrastructure, network and service components.
Compute assets are sourced from cmdb_ci_computer and its derived classes, including physical and virtual servers such as Windows, Linux and ESX systems, as well as cmdb_ci_vm_instance and other workstation or endpoint classes.
Network infrastructure is synchronized from the cmdb_ci_netgear hierarchy, covering routers, firewalls, switches and wireless access points. To support interface-level correlation, data is also ingested from cmdb_ci_network_adapter.
Service and platform components are included through classes such as cmdb_ci_database and cmdb_ci_lb_service, while additional operational assets are sourced from cmdb_ci_printer and cmdb_ci_security.
This focused set of CMDB classes ensures reconciliation reflects the assets and services that most directly impact network visibility, operations and security.
Asset Categorization and Visibility Gaps
As part of the reconciliation process, assets are automatically categorized based on their presence in ServiceNow and their visibility on the network. Assets that appear in both systems confirm where the CMDB is accurate and reliable. Assets that exist in ServiceNow but are no longer observed on the network often indicate stale or decommissioned records that were never removed. Equally important are assets that are active on the network but missing from ServiceNow altogether, revealing blind spots that can affect security posture, incident response and audit readiness.
This categorization helps teams quickly understand not just that discrepancies exist, but also the nature and impact of each discrepancy.
Understanding the CMDB Reconciliation Monitor
At the heart of this capability is the CMDB reconciliation monitor, which provides an at-a-glance view of CMDB accuracy. Instead of requiring teams to sift through thousands of configuration items, the monitor summarizes how closely ServiceNow aligns with what Infoblox observes on the network.
The monitor highlights the proportion of assets that are consistent across both systems, those that appear only in ServiceNow and those that are active on the network but missing from the CMDB. This high-level visibility makes CMDB health immediately apparent and allows teams to identify whether accuracy is improving or degrading over time.
Because the monitor is continuously updated, it also acts as an early warning system. Sudden shifts in accuracy can signal untracked infrastructure changes, discovery failures or gaps in operational workflows.
The monitor can be found on Asset Workspace under Network:
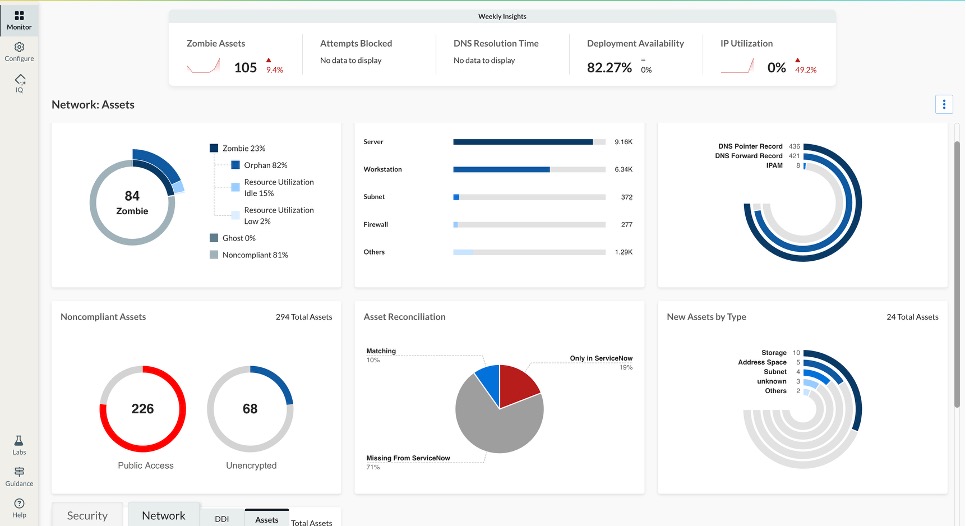
Figure 2. Asset Workspace
How to Read and Act on Monitor Data
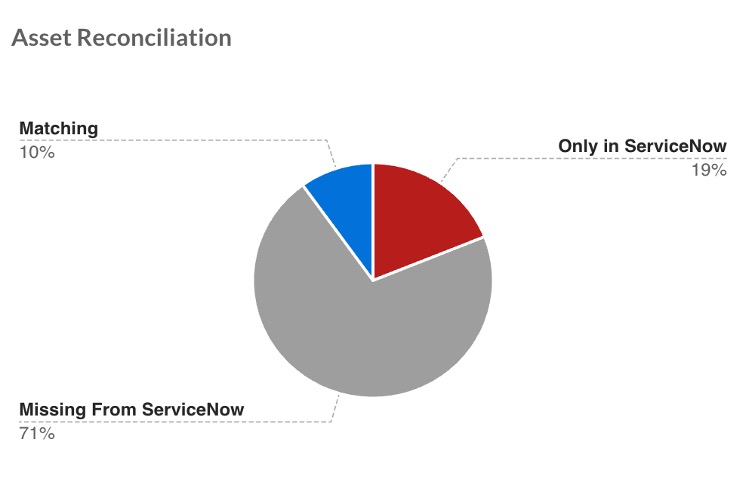
Figure 3. Asset Reconciliation monitor
Interpreting the monitor data is straightforward and actionable. A high percentage of assets present in both ServiceNow and Infoblox indicates strong CMDB hygiene and reliable downstream automation. Assets listed in ServiceNow but not observed on the network typically point to stale records that should be reviewed for retirement or cleanup. Assets that are active on the network but missing from ServiceNow often require immediate attention, as they represent visibility gaps with potential security, compliance and operational implications.
From the monitor, teams can drill into detailed reconciliation reports that identify the exact assets contributing to each category. These reports provide the evidence required to take confident action whether that means updating CMDB entries, investigating unauthorized infrastructure or validating discovery coverage. Reports can be exported or scheduled, ensuring continuous oversight of CMDB quality.

Figure 4. Options for generating reports
Conclusion
From Periodic Cleanup to Continuous CMDB Accuracy
CMDB accuracy is not achieved through one-time reconciliation efforts. Environments evolve constantly, and asset data must evolve with them. By continuously measuring ServiceNow CMDB data against Infoblox’s authoritative discovery, organizations shift from reactive cleanup to proactive data governance.
The result is a CMDB that teams can trust. Incidents are resolved faster, change decisions are made with greater confidence and security teams gain clearer visibility into what truly exists in the environment. With Infoblox, ServiceNow CMDB reconciliation becomes a living process, one that keeps pace with modern, dynamic infrastructure and restores the CMDB to its role as a dependable source of truth.
Learn More
To explore ServiceNow CMDB reconciliation and related capabilities in more detail, the following resources may be helpful:
- Not a customer? You can check out the integration by registering for a free trial.
- Visit the Ecosystem Portal to learn more about the integration.
- Check out the high-level overview and demos showcasing CMDB reconciliation and asset visibility capabilities here.
- For detailed, step-by-step guidance on configuring the ServiceNow provider and downloading or scheduling reconciliation reports, refer to the deployment guide here.